Hominoid-Specific De Novo Protein-Coding Genes Originating from Long Non-Coding RNAs
2012-09-13
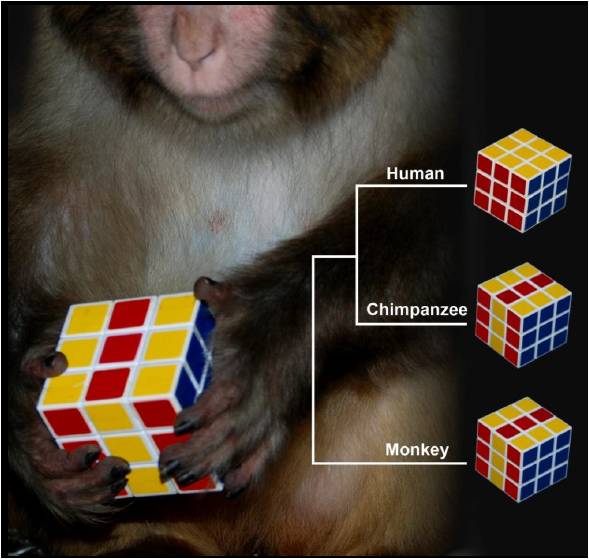
Credit: Chuan-Yun Li
As reported in the online edition of PLoS Genetics on September 13, 2012, we performed a comparative transcriptome study in human, chimpanzee, and rhesus macaque, and found that most of the hominoid-specific de novo protein-coding genes encoded long non-coding RNAs in rhesus macaque or chimpanzee. Our results suggested that a portion of long non-coding RNAs may serve as a birth pool for protein-coding genes, which are further optimized at the transcriptional level.
For details, refer to the publication:
Hominoid-Specific De Novo Protein-Coding Genes Originating from Long Non-Coding RNAs. PLoS Genetics (2012) doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002942.Chen Xie,Yong E. Zhang,Jia-Yu Chen,Chu-Jun Liu,Wei-Zhen Zhou,Ying Li,Mao Zhang,Rongli Zhang,Liping Wei,Chuan-Yun Li
Abstract:
Tinkering with pre-existing genes has long been known as a major way to create new genes. Recently, however, motherless protein-coding genes have been found to have emerged de novo from ancestral non-coding DNAs. How these genes originated is not well addressed to date. Here we identified 24 hominoid-specific de novo protein-coding genes with precise origination timing in vertebrate phylogeny. Strand-specific RNA-Seq analyses were performed in five rhesus macaque tissues (liver, prefrontal cortex, skeletal muscle, adipose, and testis), which were then integrated with public transcriptome data from human, chimpanzee, and rhesus macaque. On the basis of comparing the RNA expression profiles in the three species, we found that most of the hominoid-specific de novo protein-coding genes encoded polyadenylated non-coding RNAs in rhesus macaque or chimpanzee with a similar transcript structure and correlated tissue expression profile. According to the rule of parsimony, the majority of these hominoid-specific de novo protein-coding genes appear to have acquired a regulated transcript structure and expression profile before acquiring coding potential. Interestingly, although the expression profile was largely correlated, the coding genes in human often showed higher transcriptional abundance than their non-coding counterparts in rhesus macaque. The major findings we report in this manuscript are robust and insensitive to the parameters used in the identification and analysis of de novo genes. Our results suggest that at least a portion of long non-coding RNAs, especially those with active and regulated transcription, may serve as a birth pool for protein-coding genes, which are then further optimized at the transcriptional level.